Drug Action
antibiotics, therapeutics and their molecular targets
Medical science has discovered how to modulate the action of molecules that are misbehaving and causing disease. Medicines range from painkillers that block the action of pain-signaling molecules to antibiotics that kill pathogens by blocking their essential molecules. Atomic structures allow medical researchers to improve these drugs and to discover new ones.
Molecule of the Month Articles (35)
 |
Actinomycin
Some antibiotics attack cells by intercalating between the bases in a DNA double helix |
 |
Adrenergic Receptors
Adrenaline stimulates a G-protein-coupled receptor, priming us for action |
 |
Aminoglycoside Antibiotics
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria build enzymes that destroy drugs like streptomycin |
 |
Aminoglycoside Antibiotics and Resistance
Bacteria become resistant to aminoglycosides by destroying them or changing their target. |
 |
Anaphase-Promoting Complex / Cyclosome
APC/C guards the checkpoints that regulate key steps in the cell cycle |
 |
Beta-secretase
Beta-secretase trims proteins in the cell and plays an important role in Alzheimer's disease |
 |
Capturing Beta-Lactamase in Action
Researchers visualize the mechanism of antibiotic resistance |
 |
Circadian Clock Proteins
Circadian clock proteins measure time in our cells |
 |
Click Chemistry
A modular approach to chemistry simplifies the construction of complex protein-targeting molecules. |
 |
Cyclooxygenase
Aspirin attacks an important enzyme in pain signaling and blood clotting |
 |
Cytochrome p450
Cytochrome p450 detoxifies and solubilizes drugs and poisons by modifying them with oxygen |
 |
Dihydrofolate Reductase
DHFR is a target for cancer chemotherapy and bacterial infection |
 |
Estrogen Receptor
Estrogen binds to receptors in the nucleus and affects key genes in development |
 |
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
Popular and effective drugs for the treatment of obesity and diabetes |
| Glucocorticoid Receptor and Dexamethasone
An anti-inflammatory drug has given us a new way to fight the COVID-19 pandemic. |
|
 |
Glutamate-gated Chloride Receptors
The antibiotic ivermectin attacks glutamate-gated chloride channels, paralyzing parasitic worms. |
 |
Glutathione Transferases
Glutathione transferase tags toxic molecules, making them easy to recognize and remove. |
 |
Histone Deacetylases
Histone deacetylases regulate access to genetic information by modifying histones |
 |
HIV Envelope Glycoprotein
Envelope protein attaches HIV to the cells that it infects and powers fusion of the virus with the cell membrane |
 |
Influenza Neuraminidase
Neuraminidase is an important target for influenza drugs |
 |
Integrase
HIV integrase allows HIV to insert itself into the genome of an infected cell |
 |
Interferons
Interferons mobilize defenses against viral infection |
 |
Lactate Dehydrogenase
Our cells temporarily build lactate when supplies of oxygen are low |
 |
Microtubules
The largest filaments of the cytoskeleton provide tracks for transport throughout the cell |
 |
Multidrug Resistance Transporters
Many bacteria use multidrug resistance transporters to pump drugs and poisons out of the cell |
 |
Neurotransmitter Transporters
Neurotransmitters are transported out of nerve synapses to end a signal transmission |
 |
New Delhi Metallo-Beta-Lactamase
Antibiotics can save lives, but antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria pose a dangerous threat |
 |
Nitric Oxide Synthase
Nitric oxide gas is used as a rapid-acting hormone and as a powerful defense |
 |
Opioid Receptors
Morphine and other opioid drugs bind to receptors in the nervous system, controlling pain |
 |
P-glycoprotein
P-glycoprotein pumps toxic molecules out of our cells |
 |
Penicillin-binding Proteins
Penicillin attacks the proteins that build bacterial cell walls |
 |
Ribosome
Ribosomes are complex molecular machines that build proteins |
 |
Serotonin Receptor
Serotonin receptors control mood, emotion, and many other behaviors, and are targets for many important drugs |
 |
Tetrahydrobiopterin Biosynthesis
Tetrahydrobiopterin plays an essential role in the production of aromatic amino acids, neurotransmitters and nitric oxide. |
 |
Vancomycin
The antibiotic vancomycin blocks the construction of bacterial cell walls. |
Learning Resources (19)
 |
Award-winning HIV Enzyme Illustration
Poster
Video stills of three HIV enzymes are among the 2016 Winners of FASEB's BioArt Competition. The stills are from a molecular animation created by Maria Voigt and David Goodsell that illustrates A Molecular View of HIV Therapy.
|
 |
How do Drugs Work?
Flyer
PDB structures are used to discuss antibiotics and antivirals, chemotherapy, drug metabolism, drugs of signaling proteins, and lifestyle drugs.
|
 |
2016 A Year in Protein-Drug Complexes
Calendar
PDB structures allow us to see how drugs bind to their protein targets in exquisite detail. Available as a PDF and PowerPoint.
|
 |
The Ribosome
Flyer
This flyer commemorates the 2009 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for studies of the structure and function of the ribosome.
|
| Glucagon-like Peptide-1 and Diabetes
Poster
Image of GLP-1 receptor recognizing a GLP-1 analog (yellow) with liraglutide.
|
|
 |
How Do Drugs Work?
Poster
PDB structures are used to discuss antibiotics and antivirals, chemotherapy, drug metabolism, drugs of signaling proteins, and lifestyle drugs.
|
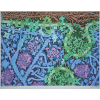 |
Insulin and Diabetes
Poster
Structural biology has revealed the details of insulin signaling and how this knowledge is being used to create new and better treatments for diabetes.
|
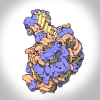 |
Ribosomal Subunits
GIF
Atomic structures of the ribosomal subunits reveal a central role for RNA in protein synthesis. Ribosomes are complex molecular machines that build proteins.
|
 |
Caffeine and Adenosine: Antagonist and Agonist
Video
This short video uses the example of adenosine and caffeine to introduce two key concepts in pharmacology: the agonist and the antagonist. Both, adenosine, and caffeine molecules bind to adenosine receptors on the neurons. Caffeine, the antagonist, blocks the receptor, while adenosine, the agonist, produces the biological response upon binding.
|
 |
Opioids and Pain Signaling
Video
Pain is one of the most trying experiences of life. On the cellular level it is communicated via special neuronal pathways. On the molecular level, however, pain is communicated like any other sensation, via a set of electrical and chemical signals facilitated by complex molecular machinery. These signals can be modulated by opioids, causing us to feel less pain, or no pain at all. Learn how opioids activate the G-proteins which in turn interact with other proteins to edit the pain signal.
|
 |
Immunology and Cancer
Video
This three-part series explores the human immune response to cancer focusing on cellular and molecular details of the process.
|
| Target Zero: Preventing HIV Transmission Documentary
Video
Target Zero shows the challenge and emotional complexity of the fight to control HIV infection.
|
|
| Penicillin and Antibiotic Resistance
Video
Since its discovery in 1928, penicillin and penicillin-related antibiotics helped save countless lives from bacterial infections. However, in the face of overuse and misuse of antibiotics, bacteria evolved resistance mechanisms that allow them to proliferate even in the presence of the newest antibiotics.
|
|
 |
A Molecular View of HIV Therapy
Video
After HIV enters a T-cell, three enzymes play essential roles in the life cycle of the virus. Reverse transcriptase copies the viral RNA genome and makes a DNA copy. Integrase inserts this viral DNA into the cell’s DNA. In the last steps of the viral life cycle, HIV protease cuts HIV proteins into their functional parts.
Current antiretroviral drugs target these three enzymes, hindering the virus reproduction. However, enzymes can mutate and become drug resistant, making it vital to use a combination of different drugs that target multiple enzymes.
This animation was created using many PDB entries for Reverse Transcriptase (3hvt, 3dlk, 3v6d, 3v4i, 3klg, 3v81), Integrase (3os1, 3os0, 3oya), Protease (3pj6, 1kj4, 1hxb, 2az9, 2azc), HIV Polyprotein (1l6n), Capsid Protein (2m8l), and Matrix Protein (1tam).
|
 |
Learn about HIV from the RCSB Protein Data Bank
Video
Use the RCSB PDB Resources to Learn about HIV
|
 |
2021 Molecular Mechanisms of Drugs for Mental Disorders
Video
|
 |
2019 Mechanisms of Bacterial Resistance to Aminoglycoside Antibiotics
Video
|
| Bound! Protein-drug matching game
Other Resource
Bound! is a card game for students 12 and up, where players compete to match the most drugs to their protein targets.
|
|
| Dexamethasone and Cytokine Storms
Article
Preventing too much of a good thing during SARS-CoV-2 infection
|
Curriculum Resources (2)
Structural Biology Highlights (4)
Global Health (14)
| Diabetes Mellitus - Sitagliptin
An oral non-substrate-like DPP-4 inhibitor used for treating diabetes.
|
|
| Diabetes Mellitus - Vildagliptin
An oral substrate-like DPP-4 inhibitor used for treating diabetes.
|
|
| Diabetes Mellitus - Saxagliptin
An oral substrate-like DPP-4 inhibitor used for treating diabetes.
|
|
| Diabetes Mellitus - Alogliptin
An oral xanthine based DPP-4 inhibitor used for treating diabetes.
|
|
| Diabetes Mellitus - Linagliptin
An oral xanthine based DPP-4 inhibitor used for treating diabetes.
|
|
| Diabetes Mellitus - Anagliptin
An oral non-substrate-like DPP-4 inhibitor used for treating diabetes.
|
|
| Diabetes Mellitus - Acarbose
An oral substrate-like glucosidase inhibitor used for treating diabetes.
|
|
| Diabetes Mellitus - Miglitol
A small molecule glucosidase inhibitor used for treating diabetes.
|
|
| Diabetes Mellitus - Rosiglitazone
An agonist for PPAR-g receptor used for treating diabetes
|
|
| Diabetes Mellitus - Insulin
This is a polypeptide hormone, critical for glucose uptake by cells.
|
|
| Diabetes Mellitus - Insulin Lispro
This designed molecule is a rapid-acting human insulin analog
|
|
| Diabetes Mellitus - Insulin Aspart
This designed molecule is a rapid-acting human insulin analog
|
|
| Diabetes Mellitus - Insulin Detemir
This designed molecule is a long-acting human insulin analog
|
|
| Diabetes Mellitus - Insulin Degludec
This designed molecule is an ultra-long acting human insulin analog
|
Goodsell Molecular Landscapes (2)
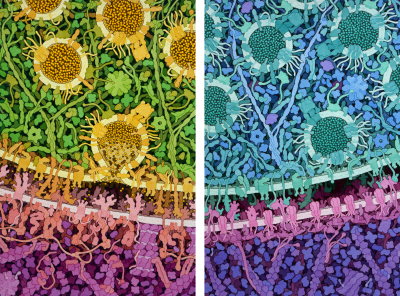 |
Excitatory and Inhibitory Synapses
Excitatory and Inhibitory Synapses (2018) by David S. Goodsell
|
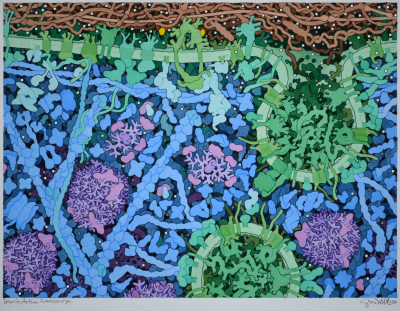 |
Insulin Action
Insulin Action (2016) by David S. Goodsell.
|